¿QUÉ ES EL CIC Y CÚAL ES SU IMPORTANCIA?
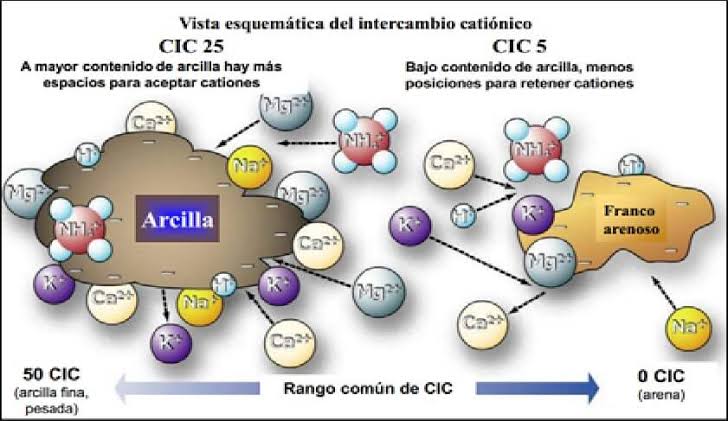
Es una propiedad del suelo que junto con el pH, nutrientes para las plantas, salinización etc. conforman a las “Propiedades Químicas Del Suelo”, pero primero definamos que es el CIC, bueno se define como “La cantidad total de cargas negativas que están disponibles sobre la superficie de partículas en el suelo” (INTAGRI, 2015). Para entender esto, las partículas como las Arenas, Limos, Arcillas y La Materia Orgánica están cargadas negativamente, cada una de las partículas tiene un valor diferente, siendo el Arenoso el más bajo siendo 1-5 meq/100 gr, seguido de las Arcillas (entre 10-150 meq/100gr) y el que presenta el mayor CIC es la Materia Orgánica, teniendo valores de 200-400 meq/100 gr, pero, ¿estos valores qué significan?, bueno las partículas las dividimos en CATIONES (Carga +) y los ANIONES (Carga Negativa) las partículas como Arenas, Limos, Arcillas y La Materia Orgánica están cargadas (-) y en el suelo hay Cationes como: K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, Al 3+ y H+ que son predominantes en suelos agrícolas, entonces la mayor parte de los nutrientes están adheridos a las superficies de las partículas del suelo, entonces la CIC proporciona una reserva de nutrientes para reponer nutrientes que fueron absorbidos por las plantas o lavados.
FACTORES QUE AFECTAN EL CIC
Como es algo relacionado con las partículas del suelo, muchos de los factores están relacionados con estas, por ejemplo, el tamaño de la partícula, esto porque entre más pequeña sea la partícula, será más grande la CIC, y está muy claro porque como vimos arriba las Arcillas tienen mayor CIC que las arenas, la Naturaleza de las partículas, es decir la composición y su estructura influirá en las posibilidades de cambio de sus cationes. El pH como en básicamente todos los procesos se ve involucrado, en esta ocasión nos altera el CIC en suelos ácidos, esto debido a una reacción conocida como “Acidez Intercambiable” que es la suma de los Cationes Al y Cationes H de esta manera evitando que otros Cationes tomen el lugar en las partículas del suelo.
¿CÓMO AUMENTAR EL CIC?
Cómo vimos al principio lo que nos da una mayor CIC es la Materia Orgánica, por esta y muchas otras, es una parte súper importante en nuestro suelos y tener un porcentaje mayor al 3% aumentará nuestra fertilidad de nuestros suelos reteniendo y poniendo a disposición los nutrientes para nuetro cultivo, pero , ¿Cómo se puede aumentar? Mediante la aplicación de productos que nos eleven el % de M.O, como lo son las Compostas, y en Micorrizas Suppra contamos con composta a base de bagazo de Agave y caña. Otro factor muy importante es los mediar el uso de Fertilizantes que produzcan o tengan Amoniaco, esto porque al momento de hacer la nitrificación, se liberan iones H+, que son los responsables de acidificar el suelo por lo que es recomendable mediar su uso y ahora más que nunca con la alza exponencial que han tenido estos productos, por lo que debemos buscar productos que nos permitan disminuir el uso de Fertilizantes, como es el caso de Micorrizas Suppra, nuestras perfectas aliadas contra esta crisis y bajar el consumo de Fertilizantes no sólo por no alterar nuestro pH sino para no alterar nuestro bolsillo con estos precios exorbitantes.

LET’S TALK ABOUT: CATION EXCHANGE CAPACITY (CEC)
WHAT IS CEC AND WHAT IS ITS IMPORTANCE?
Its a property of the soil that, together with the pH, nutrients for plants, salinization, etc., make up the chemical properties of the soil, but first, lets define CEC. Its defined as the total amount of negative charges that are available on the surface of particles in the soil. To understand this, particles such as sand, silt, clay and organic matter are negatively charged, each of the particles has a different value, with sandy being the lowest with 1-5 meq/100 gr, followed by silt, and the organic matter has the highest CEC with 200-400 meq/100 gr, but, what does this values mean?
Well, the particles are divided into CATIONS (Positive Charge) and ANIONS (Negative Charge). Particles such as Sand, Lime, Clay and Organic Matter are charged (-) and in the soil there are Cations such as: K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+ , Al 3+ and H+ which are predominant in agricultural soils, so most of the nutrients are attached to the surfaces of soil particles, so the CEC provides a nutrient pool to replenish nutrients that were taken up by plants or washed away

FACTORS AFFECTING THE CIC
As its something related to soil particles, many of the factors are related to them, for example, the size of the particle, this is because the smaller the particle, the larger the CEC, and it is very clear because as we saw above clays have higher CEC than sands, the nature of the particles, the composition and its structure will influence the possibilities of change of its cations. The pH is basically involved in all the processes, on this occasion the CEC in acid soils is altered, this due to a reaction known as “Exchangeable Acidity” which is the sum of the Cations Al and Cations H in this way avoiding that other cations take the place in the soil particles.
HOW TO INCREASE THE CEC?
As we saw at the beginning, what gives us a higher CEC is Organic Matter, for this and many others, it is a super important part of our soils and having a percentage greater than 3% will increase our soil fertility by retaining and making available the nutrients for our crop, but how can it be increased? Through the application of products that raise the % of OM, such as Composts, and at Micorrizas Suppra we have compost based on Agave bagasse and cane. Another very important factor is mediating the use of fertilizers that produce or have ammonia, this is because at the time of nitrification, H+ ions are released, which are responsible for acidifying the soil, so it is advisable to mediate their use and now more than ever with the exponential rise that these products have had, so we must look for products that allow us to reduce the use of Fertilizers, as is the case of Mycorrhizae Suppra, our perfect allies against this crisis and lower the consumption of Fertilizers not only for not to alter our pH but not to alter our pocket with these exorbitant prices.
